Do Eustachian tubes block? A critical look into the blocked Eustachian tube causes, symptoms, clearing, treatment as well as a clear look into home remedies.
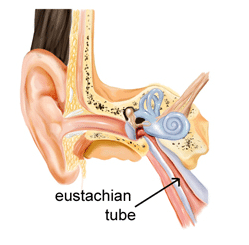
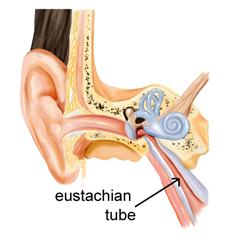
blocked eustachian tube
This tubes usually connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. They help the ears drain fluid at all times. They ventilate the middle ear space. Sometimes it requires that a mouth is opened, the tubes open freely to let the air in to let the pressure in the middle ears equal to the pressure outside of the ears, the pressure outside of the ear at times get too high causing ear pain and thus troubled hearing.
Causes of Blocked Eustachian Tube
Eustachian tubes can be blocked due to various reasons include the following;
- Swelling from a cold can lead to blocked Eustachian tube; The most common cause of the blockage is cold also known as the upper respiratory infection
- Allergies or a sinus infection can keep the Eustachian tubes from opening leading to pressure changes and fluid collecting in the middle ear. The fluid in the ear can cause infection known as acute otitis media especially to young children because their tubes are shorter and more easily blocked. Allergies that affect the nose, such as persistent rhinitis and hay fever, can cause extra mucus and inflammation in and around the Eustachian tube and lead to ETD.
Adenoid tissue in the back of the nose near the Eustachian tube can act as a reservoir for bacteria, contributing to recurrent ear infections. Enlarged adenoids obstructing the opening of the Eustachian tube may also be present
- Rarely, but at times, masses or tumors in the skull base or nasopharynx can lead to Eustachian tube obstruction. This is serious and may require urgent medical attention.
- The size and shape of the Eustachian tube is different in children than in adults. This accounts for the fact that serous otitis media is more common in very young children. Some children inherit small Eustachian tubes from their parents; this accounts in part for the familial tendency to middle ear infection. As the child matures, the Eustachian tube usually assumes a more adult shape. Blocked Eustachian is however different to people depending on exact cause.
- Blocked Eustachian tube is more common in the child with a cleft palate. This is due to the fact that the muscles that move the palate also open the Eustachian tube. These muscles are deficient or abnormal in the cleft palate child.
- The lining membrane (mucous membrane) of the middle ear and Eustachian tube is connected with, and is the same as, the membrane of the nose, sinuses and throat. Infection of these areas results in mucous membrane swelling which in turn may result in Eustachian tube obstruction
- Allergic reactions in the nose and throat result in mucous membrane swelling, and this swelling may also cause blocked Eustachian tube. This reaction may be acute, as in hay fever type reaction, or may be chronic, as in many varieties of “chronic sinusitis”.
- The adenoids are located in the nasopharynx, in the area around and between the Eustachian tube openings. When enlarged, the adenoids may lead to blocked Eustachian tube opening. It can be a symptom of rare tumors in the back of the nose, though these usually cause other symptoms in addition to blockage of the Eustachian tube.
- The eardrum can also become perforated by changes in the surrounding air pressure when the airplane is landing or when the diver is diving. If the Eustachian tube cannot adjust to the pressure in the ear fast enough, the ear drum could rapture rip apart, sometimes the cause of eardrum rapture is a combination of the blocked Eustachian tube infection and changes in the surrounding air pressure.
Symptoms of Blocked Eustachian Tube
When Eustachian tubes block, symptoms can last for a few hours to several weeks or even more depending on the cause, most cases due to a cold being the common cause the symptoms are likely to go away within a week they can cause several symptoms, including;
- Ears that hurt and feel full.
- Ringing or popping noises in your ears also known as tinnitus, this usually happens when symptoms are easing, over time, a person with a perforated eardrum may notice hearing loss.
- Hearing problems.
- Feeling a little dizzy
- The main symptom is muffled or dulled hearing.
- You may also experience ear pain because the ear drum is tensed and stretched
- Moderate to severe hearing loss
- A clear pus-filled or bloody drainage may come out of the ear
- Stiff neck
- Severe headache
- Difficulty in talking or opening of the mouth
- Vomiting
- Pain in the bone behind the ear
- Sudden changes in vision and
- Numbness in the face.
A blocked Eustachian tube, raptured tympanic membrane or eardrum, is not usually a serious condition, in many cases it heals on its own but if it doesn’t heal and the rapture becomes larger from repeated infections or trauma, it could have serious complications.
Blocked Eustachian Tube Medical Treatment
treatment for blocked eustachian tube
Allergic Treatment and Nasal Decongestion.
Identification and treatment of nasal allergies may also help to reduce the swelling in the lining of the Eustachian tube. Identifying the particular allergen a patient is sensitive to and eliminating it from the environment may reduce the patient’s symptoms. Allergy shots may also provide some help, although it may take a long time to notice beneficial effects.
Intranasal steroids act to reduce inflammation of the mucosal lining of the nose and may provide some benefit to patients with Eustachian tube dysfunction. This helps about 50 percent of patients with Eustachian tube dysfunction secondary to allergies.
A trial of two weeks of daily usage is recommended to see if the medication is helpful. Nasal steroids take this long to begin to work. The onset of their effects is gradual, so patients have to use it every day. One does not typically notice an immediate improvement after spraying it in their nose. This is however vital to helping in blocked Eustachian tube.
Decongestants constrict blood vessels and help open the Eustachian tube by reducing swelling of the lining of the nose. These medications work immediately and can be taken as needed. Oral preparations work for about four hours and should not be used around bedtime because they may make it difficult to get to sleep.
Nasal spray preparations work quite well and directly decongest the nose; however, because the body rapidly gets used to the medication, they should only be used for up to three days in a row. Antihistamines work to reduce the body’s inflammatory response to allergens.
These medications may be helpful for some patients, although in my experience, not as reliably as nasal steroids or decongestants. Antihistamines can be taken as needed.
Blocked Eustachian tubes often get better on their own. You may be able to open the blocked tubes with a simple exercise. Close your mouth, hold your nose, and gently blow as if you are blowing your nose.
Treatment of the blocked Eustachian tube is not very sophisticated or effective.
For the usual type of ETD (closed), medications for allergy such as decongestants, systemic or local antihistamines and nasal topical steroids are commonly tried.
Closed Eustachian Tube
Occasionally, people with severe symptoms due to Eustachian Tube dysfunction may have a ventilation tube placed in their ear drum.
This relieves the symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction but creates a perforation in the eardrum which reduces hearing to a small extent as well as provides a potential entry point for infection. However, in most cases, it is worth it to find out if symptoms respond to ventilation of the ear.
Recently Balloon Eustachian Tuboplasty (BET) has been used as a method of treating chronic obstructive Eustachian tube.
Patulous Eustachian tube.
Methods of treatment aimed at “patulous” (abnormally open) Eustachian tubes include Premarin nose drops or nasal spray, and insufflation of boric acid and salicylate powder. These agents are intended to close Eustachian tubes, and would not be appropriate for persons who have plugged Eustachian tubes rather than abnormally open ones.
As a last resort, a patulous Eustachian tube may be closed surgically and a perforation created in the eardrum. However, it is difficult to imagine a situation where this would be desirable
Also the below alternatives are advised to treat a poorly performing Eustachian tube;
- An abnormally narrow Eustachian tube can sometimes be enlarged with medicines. Nasal steroid sprays are frequently tried, and in adults nasal and oral decongestants may be recommended.
- If an infection is thought to be present (otitis media), then antibiotics are appropriate. However, if middle ear fluid persists after more than one course of antibiotics, additional trials of antibiotics are much less efficacious in relieving the problem
- If allergies are thought to be contributing to the Eustachian tube dysfunction, allergy testing (which can be performed through our office) and allergy treatment may be indicated.
If symptoms continue or the cause of the ETD is not clear, you may be referred to an ear specialist for assessment. Treatment options depend on any underlying cause that may be found. A treatment recently developed is called balloon dilatation.
This involves inserting a tiny tube with a small balloon on the end into the Eustachian tube through the nose. The balloon is filled with salt water and left in place for a few minutes in order to stretch the Eustachian tube. Currently the treatment is only being used as part of research but may be authorized for general use if trials are favorable.
Home Remedies for Blocked Eustachian Tube
Sometimes Eustachian tubes can block while at home, and thus no medical attention is required before the below self-diagnosis is tried;
Self-Inflation of the Ears: It is possible to forcibly blow air through the Eustachian tube into the middle ear by pinching the nose closed and “popping the ear.” Another way to do this is to blow up balloons. The pressure required to expand a balloon is usually enough to push air up the Eustachian tube. This is a very useful maneuver and may be repeated as often as necessary, whenever a sense of pressure or fullness in the ear develops. This should not be performed when a cold or nasal discharge is present as this may drive infected mucous into the middle ear and cause an ear infection thus assisting the blocked Eustachian tube.
Nasal spray: Blocked Eustachian tube can cause cracking noises, given that its structure is usually lined with mucosa which is always supposedly moist, sometimes the surface may become sticky from inflammation such that any movement whether an opening motion or sliding would cause crackling noise, the treatment in this case is with steroids nasal sprays for a period of about six weeks.
Decongestant tablets (e.g. Sudafed); Tablets may reduce swelling in the tubes if used regularly for two weeks. Those with high blood pressure should use these for 7 days only. Over-the-counter sprays can be helpful, but should only be used for 5 days at a time as longer use may cause worse rebound congestion.
Guaifenesin (e.g. plain Mucinex or Robitussin). This thins mucus if you drink extra water while taking it. Thinner mucus is less likely to stick in the Eustachian tubes
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Treatment
Chronic blockage of the Eustachian tube is called Eustachian tube dysfunction. This can occur when the lining of the nose becomes irritated and inflamed, narrowing the Eustachian tube opening or its passageway. Illnesses like the common cold or influenza are often to blame.
Pollution and cigarette smoke can also cause Eustachian tube dysfunction. In many areas of the world, nasal allergy (allergic rhinitis) is the major cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction. Obesity can also predispose a patient to Eustachian tube dysfunction because of excess fatty deposits around the passageway of the Eustachian tube. Rarely, Eustachian tube blockage may be the sign of a more serious problem such as nasal polyps, a cleft palate, or a skull base tumor.
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD), occurs when the Eustachian tube becomes blocked, if the lining of the tube swells or if the tube does not open fully to allow air to travel to the middle ear.
Colds and other nasal, sinus, ear or throat infections being the common cause of the Eustachian tubes.
The blocked nose, or thick mucus that develops during a cold or other infections, may lead to blocked Eustachian tube. An infection may also cause the lining of the Eustachian tube to become inflamed and swollen.
Most people will have had one or more episodes in their life when they have had a cold and find that they cannot hear so well due to ETD. The symptoms of ETD may persist for up to a week or so (sometimes longer) after the other symptoms of the infection have gone. This may be due to longer duration that the trapped mucus and swelling takes to clear even when the germ causing infection has gone.
Sometimes the infection may be too mild but perhaps a mild cold with mild bunged up nose.
Treatment of the ETD depends on the causes, the following outlines different causes and treatment;
- Treatment of the acute serous otitis media is usually medical and is directed mostly towards treatment of the upper respiratory infection or allergy attacks, this may include use of antibiotics, antihistamines which are usually anti-allergy drugs, decongestants (drugs to decrease the mucous membrane swelling) and nasal sprays.
- In the presence of an upper respiratory infection, such as tonsillitis, colds or sinusitis, the fluid in the middle ear may become infected, this results to what is commonly known as an abscessed ear, the infected fluid in the middle ear may cause severe pain, if an examination reveals that there is a considerable ear pressure, then a myringotomy may be necessary to relieve the pain but in most cases use of antibiotics will suffice the situation at hand.
Resolution of the acute infection of the ear occasionally leaves the patient with uninfected fluid that is found in the middle ear
- Subsiding of the acute respiratory infection may leave the patient with chronic sinus infection. Pus from the sinuses and nose drains over the Eustachian tube in the nasopharynx resulting in persistent blocked Eustachian tube, also antibiotic treatment may be indicated in this situation.
- Some patients who suffer from gastro-esophageal acid refux that allows the stomach acid to at times irritate the opening of the Eustachian tube that in most cases result in inflammation of the tube. Medical treatment for the acid reflux may be initiated in order to control this situation.
- Surgical treatment whose primary objective is to reestablish ventilation of the middle ear, keeping the hearing at normal level and preventing the recurrent infection that might damage the ear drum membrane and the middle ear bones. This sometimes involves myringotomy with insertion of the ventilation tube.
Patients who suffer from ETD are likely candidates for Eustachian tube surgery whose procedure is to widen the tube. This is done under general anesthesia in the operating room
- Abnormal patency of the Eustachian tube is a condition occurring primarily in adults in which the tube remains open for prolonged periods that causes many distressing symptoms like ear fullness and blockage, a hollow feeling like hearing one’s own breathing and voice reverbation, however it does not produce a hearing impairment.
Surgical operation and correction of this condition can be performed.
- Palatal myoclonus is a rare condition in which muscles of the palate (back of the mouth) twitch rhythmically many times a minute. The cause of this muscle spasm is unknown.
A person may experience a rhythmic clicking sound in the ear as the Eustachian tube opens and closes.
Sedatives are often recommended in controlling the symptoms. No treatment is needed in many cases
Further references;
- Eustachian tubes; Topic Overview: http://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/blocked-eustachian-tubes-topic-overview
- Hearing loss; the facts: http://www.medicinenet.com/eustachian_tube_problems/page2.htm
- Eustachian tube dysfunction: http://patient.info/health/eustachian-tube-dysfunction